The Internet can be defined as a network of computers networks (indeed a network of networks rather than a network of single computers), distributed on all the globe, that rely on a shared set of communication protocols collectively known as TCP/IP, that allows communication, exchange, storage of information for it’s connected users. Figure 1-1 illustrates the worldwide distribution of the Internet network and the fact that several, often redundant communication paths are available (symbolized by the colored lines in the figure) to connect two nodes of the network.
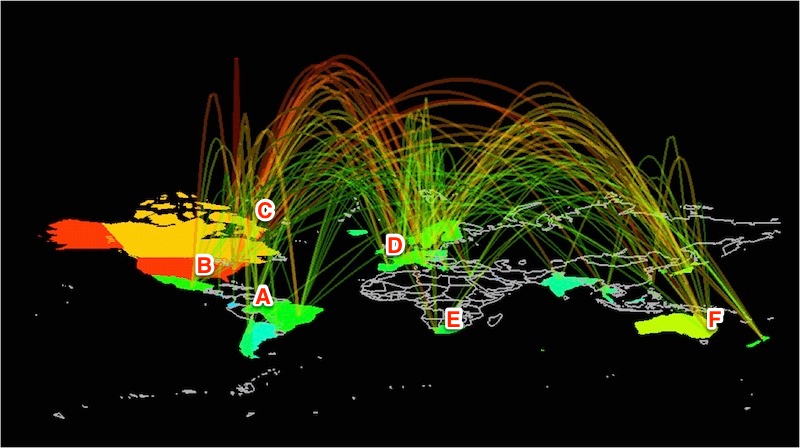
Redundancy is a basic feature of the Internet. Back in 1960, the networks that then evolved into the Internet as we are currently familiar with, were commissioned by the Government of United States in order “to build robust, fault-tolerant, and distributed computer networks” (ref: wikipedia). The reason for redundancy is that should a node of the network or a communication route stop working for any reason, the network as a whole would remain up and running. This of course has implications in case of war or catastrophic natural events.
The figure below, in which the concept of a “network of networks” can be fully appreciated, shows a 2015 map of the Internet generated by the Opte project.
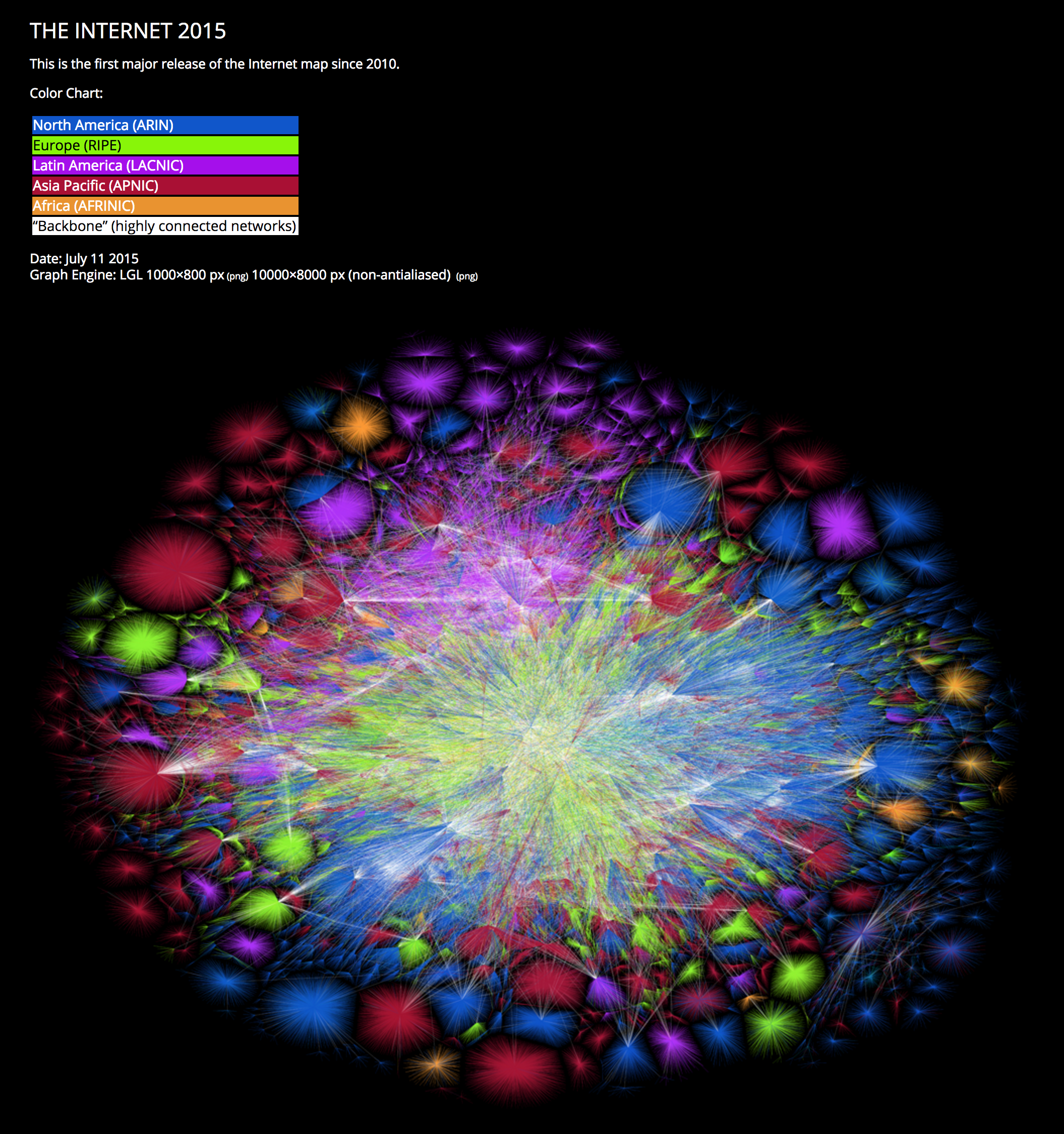
To get more information on the history and other aspects of the Internet, please visit the Internet page on wikipedia.
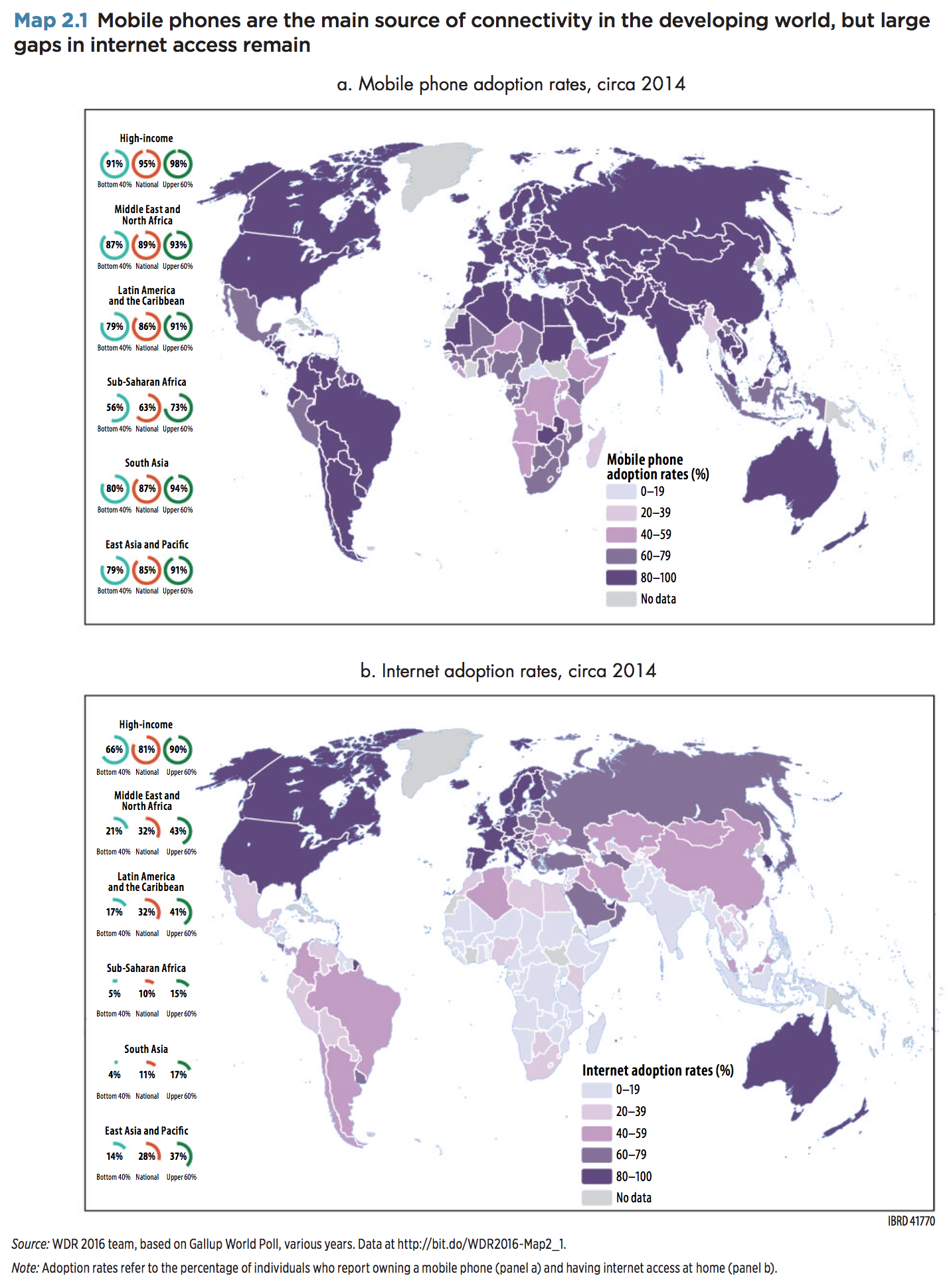
It is worth noting that the figures above underscore the existence of a strong digital divide, whereby some countries and whole areas of the world are clearly more connected to the Internet with respect to others. As shown by the next figure, from the World Development Report 2016, this technological and social gap is slowly getting narrower over time, often thanks to mobile technologies, but still a solid reality.
You can continue reading about how data is transmitted on the Internet
Chapter Sections
[subpages]